A Shifting Mosaic: The Evolution of Europe’s Map Over Time
Related Articles: A Shifting Mosaic: The Evolution of Europe’s Map Over Time
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Shifting Mosaic: The Evolution of Europe’s Map Over Time. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Shifting Mosaic: The Evolution of Europe’s Map Over Time

The map of Europe is not a static entity. It is a dynamic tapestry, woven with threads of history, conflict, and cultural exchange. Its ever-changing borders and shifting political landscapes tell a story of power, ambition, and the enduring quest for identity. From the ancient empires of Greece and Rome to the modern nation-states of today, Europe’s map has undergone a remarkable transformation.
Ancient Roots and the Rise of Empires
The earliest maps of Europe, etched in stone and clay, depict a world vastly different from our own. Ancient civilizations, like the Greeks, Romans, and Celts, carved their influence onto the land, leaving behind a legacy of cultural exchange and political dominance. The Roman Empire, at its zenith, stretched from the British Isles to the Middle East, uniting a vast expanse of territory under a single banner. This period of Roman rule left an indelible mark on the map of Europe, shaping its linguistic, cultural, and political landscape for centuries to come.
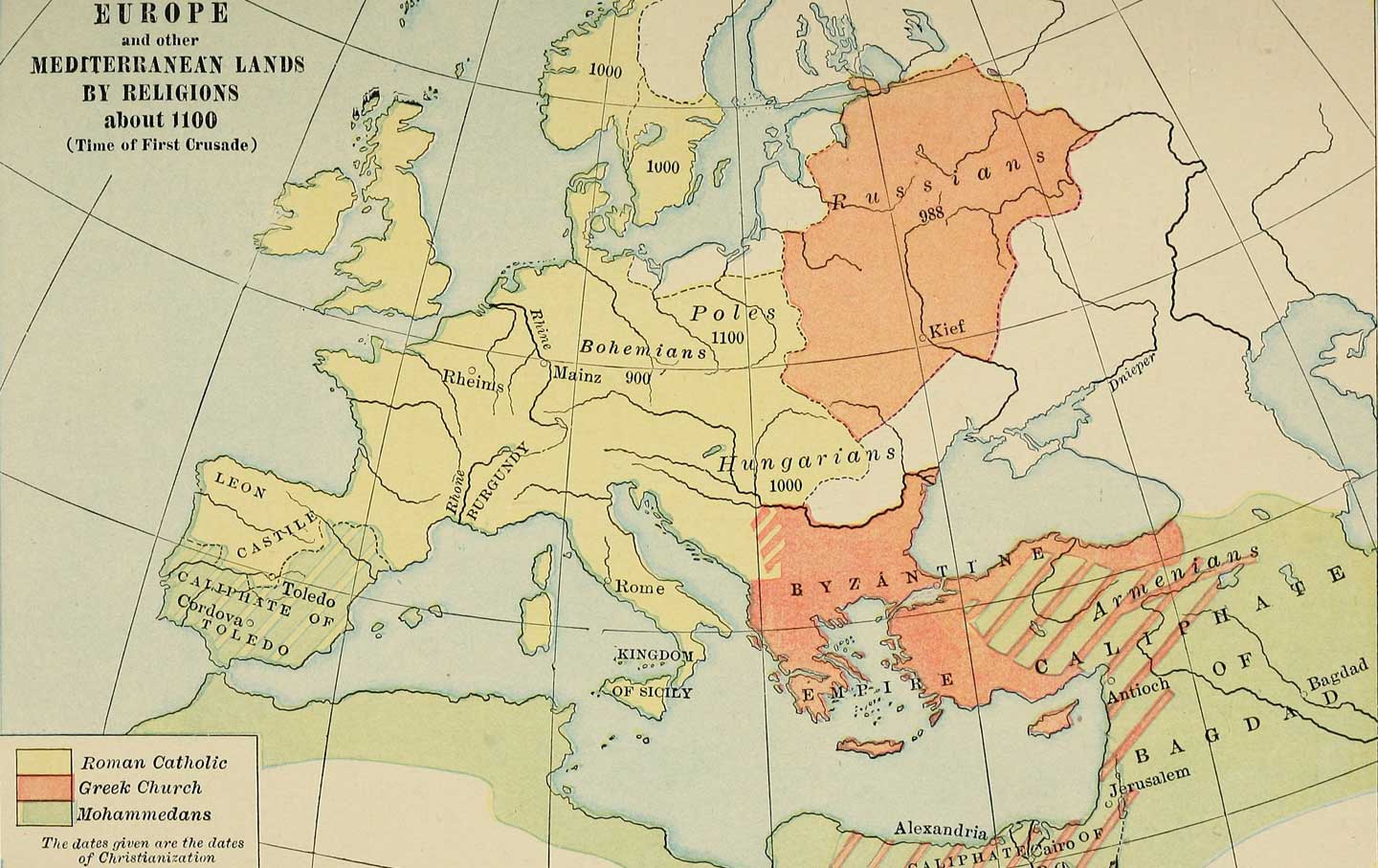
The Middle Ages: Fragmented Kingdoms and the Rise of Nationhood
The fall of the Roman Empire ushered in a new era, one marked by fragmentation and the rise of independent kingdoms. The map of Europe became a patchwork of diverse cultures and languages, each vying for power and influence. The Holy Roman Empire, a loose federation of Germanic states, attempted to recreate the grandeur of Rome, but its power waned over time. The emergence of strong monarchies in England, France, and Spain signaled a shift towards centralized power and the beginnings of national identity.
The Renaissance and Reformation: A New Era of Exploration and Conflict
The Renaissance, a period of intellectual and artistic rebirth, fueled a renewed interest in exploration and discovery. European powers, spurred by a desire for wealth and influence, embarked on voyages to distant lands, expanding their reach and altering the global map. The Reformation, a religious upheaval that challenged the authority of the Catholic Church, further fractured Europe, leading to religious wars and political instability.
The Age of Empires: Colonial Expansion and Global Dominance
The 16th and 17th centuries witnessed the rise of European empires, fueled by colonialism and the pursuit of global dominance. The map of Europe expanded beyond its traditional borders, encompassing vast territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia. The British Empire, in particular, emerged as a global superpower, its influence stretching across the globe. This era of expansion, however, also sowed the seeds of future conflict, as rival empires clashed for control of resources and territory.
The Industrial Revolution: Economic Power and the Rise of Nationalism
The Industrial Revolution, beginning in the late 18th century, transformed Europe’s economic landscape. New technologies and innovations fueled unprecedented growth, leading to a surge in population and the rise of industrial centers. The map of Europe began to reflect this economic shift, with major cities like London, Paris, and Berlin emerging as centers of commerce and industry. This period also saw the rise of nationalism, as people began to identify more strongly with their national identities, leading to demands for self-determination and the redrawing of borders.
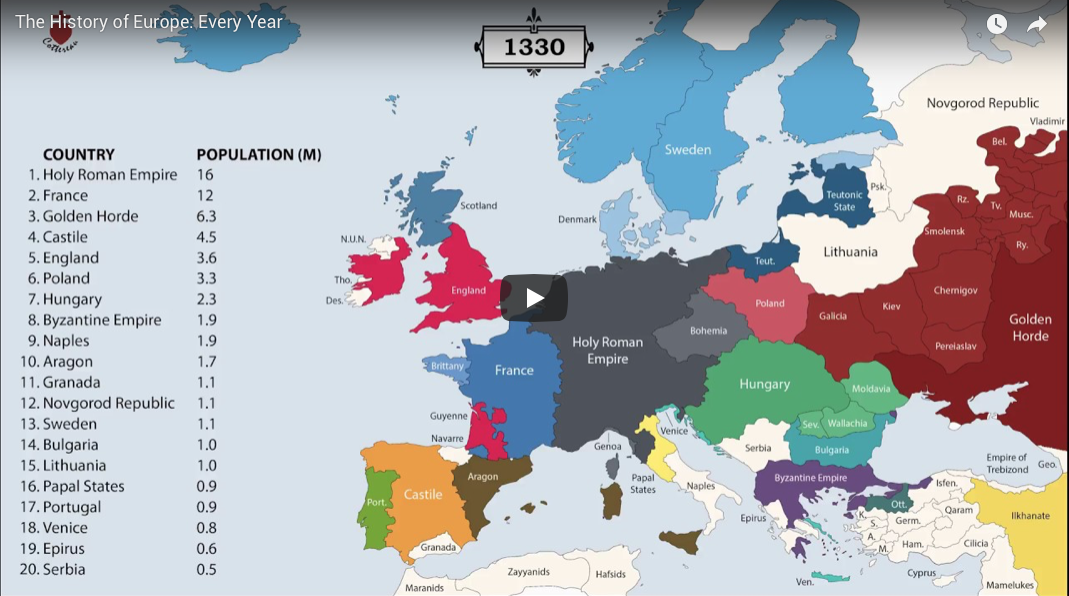
The 20th Century: Wars, Revolutions, and the Cold War
The 20th century was a tumultuous period for Europe, marked by two world wars, revolutions, and the Cold War. The First World War, a conflict that engulfed the entire continent, resulted in the redrawing of borders and the creation of new nation-states. The Second World War, even more devastating, further reshaped the map of Europe, leading to the rise of the Soviet Union as a dominant power. The Cold War, a period of ideological conflict between the Soviet Union and the West, divided Europe into two camps, with the Iron Curtain separating East and West.
The Post-Cold War Era: Reunification, Expansion, and Integration
The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 marked the end of the Cold War and ushered in a new era for Europe. The Soviet Union dissolved, and many of its former satellite states gained independence. The map of Europe was once again redrawn, with the accession of new members to the European Union. The EU, an economic and political alliance, has played a significant role in promoting peace, cooperation, and economic integration across the continent.
The Importance of the Shifting Map of Europe
The ever-changing map of Europe is a testament to the dynamism and complexity of its history. It reflects the interplay of political, economic, and social forces that have shaped the continent’s identity. Understanding the evolution of the map provides valuable insights into:
- The rise and fall of empires: The map reveals the shifting balance of power throughout history, showcasing the rise and fall of empires and the impact of their influence.
- The emergence of nation-states: The map illustrates the process by which nations have defined their borders and asserted their sovereignty, shaping the political landscape of Europe.
- The impact of conflict and cooperation: The map highlights the role of war, revolution, and diplomacy in shaping the boundaries of Europe, revealing the consequences of conflict and the benefits of cooperation.
- The influence of cultural exchange: The map reflects the interplay of cultures and languages, showcasing the diffusion of ideas and traditions across borders.
- The challenges of integration and globalization: The map illustrates the complexities of integrating diverse nations and cultures within a single framework, highlighting the challenges and opportunities of globalization.
FAQs about the Evolution of the Map of Europe
Q: What were the most significant changes to the map of Europe in the 20th century?
A: The 20th century witnessed a dramatic reshaping of the European map, driven by two world wars, revolutions, and the Cold War. The Treaty of Versailles, signed after World War I, redrew borders, creating new nations and dissolving empires. World War II led to the rise of the Soviet Union and the division of Europe into communist and capitalist blocs. The fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989 marked the end of the Cold War and the reunification of Germany, further altering the map.
Q: How has the European Union impacted the map of Europe?
A: The European Union, established in 1993, has played a significant role in shaping the map of Europe through its expansion policy. Since its inception, the EU has welcomed new members from Central and Eastern Europe, expanding its borders and integrating new nations into its economic and political framework. This expansion has fostered economic growth, political stability, and cultural exchange across the continent.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the map of Europe today?
A: The map of Europe continues to evolve, facing challenges related to globalization, migration, and political instability. The rise of nationalism and populism in some European countries has led to calls for greater autonomy and even secession, potentially impacting the future of the European Union. The ongoing refugee crisis and the influx of migrants from conflict zones have also created tensions and raised questions about the borders and identity of Europe.
Tips for Understanding the Evolution of the Map of Europe
- Study historical maps: Examining historical maps from different periods can provide valuable insights into the evolution of borders, the rise and fall of empires, and the changing cultural landscapes of Europe.
- Explore online resources: Numerous online resources, including interactive maps and timelines, can help you visualize the shifting boundaries of Europe and understand the historical context behind these changes.
- Read historical accounts: Reading primary and secondary sources can provide detailed information about the events, personalities, and political forces that shaped the map of Europe.
- Engage in discussions: Discussing the evolution of the map with others can help you gain different perspectives and deepen your understanding of the complex forces at play.
Conclusion
The map of Europe is a dynamic and ever-changing entity, reflecting the ebb and flow of history, power, and identity. From the ancient empires to the modern nation-states, the map has undergone a remarkable transformation, shaped by conflict, cooperation, and the enduring quest for self-determination. Understanding the evolution of the map provides valuable insights into the complex forces that have shaped Europe’s political, economic, and cultural landscape, offering a deeper understanding of the continent’s past, present, and future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Shifting Mosaic: The Evolution of Europe’s Map Over Time. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!