Navigating the Caribbean: A Comparative Look at the Maps of Puerto Rico and Cuba
Related Articles: Navigating the Caribbean: A Comparative Look at the Maps of Puerto Rico and Cuba
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Caribbean: A Comparative Look at the Maps of Puerto Rico and Cuba. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Caribbean: A Comparative Look at the Maps of Puerto Rico and Cuba
/Caribbean_general_map-56a38ec03df78cf7727df5b8.png)
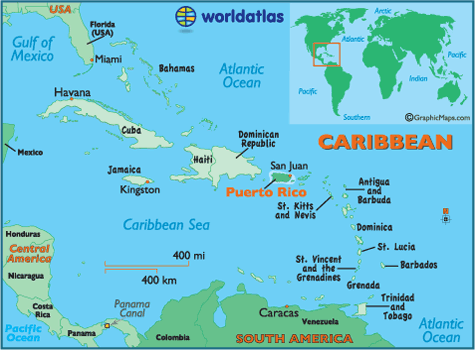
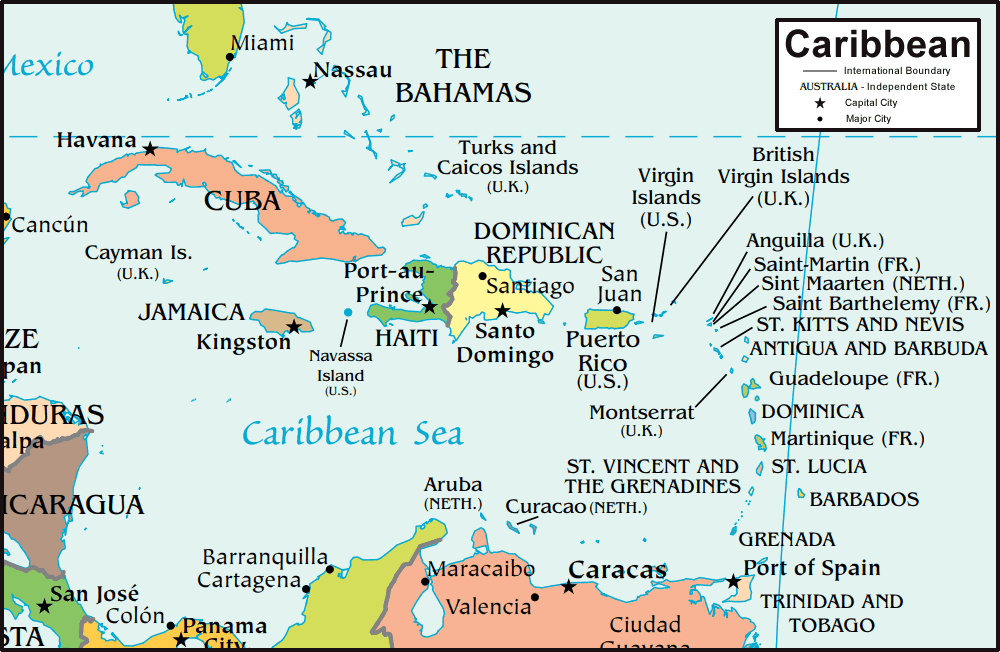
The Caribbean Sea, a vibrant tapestry of islands, boasts a rich history and diverse culture. Two prominent players in this mosaic are Puerto Rico and Cuba, each with a unique geographical identity that has shaped their destinies. Understanding the maps of these islands is crucial for appreciating their distinct features and the factors that have influenced their development.
Puerto Rico: A Compact Island with Varied Terrain
Puerto Rico, a U.S. territory, is a relatively small island, measuring approximately 100 miles long and 35 miles wide. Its compact size, however, belies its diverse topography. The island is characterized by a central mountain range, the Cordillera Central, which runs from west to east, culminating in the highest peak, Cerro Punta, at 4,389 feet. This mountainous spine divides the island into distinct geographical regions.
- The Northern Coast: This region is dominated by a narrow coastal plain, fringed by beaches and dotted with coastal towns. The terrain here is generally flat, making it suitable for agriculture and urban development.
- The Southern Coast: In contrast to the north, the southern coast features a more rugged coastline, with numerous bays, inlets, and rocky cliffs. The terrain is also more varied, with rolling hills and valleys.
- The Central Highlands: The Cordillera Central is a rugged and mountainous region, characterized by dense forests, steep slopes, and waterfalls. This region is home to numerous endemic species of flora and fauna and is a popular destination for hiking and ecotourism.
Cuba: A Larger Island with Diverse Landscapes
Cuba, the largest island in the Caribbean, is significantly larger than Puerto Rico, stretching over 750 miles long and 100 miles wide. This vast expanse gives rise to a diverse range of landscapes, from lush forests and rolling plains to rugged mountains and pristine beaches.
- The Western Region: This region is characterized by a flat, fertile plain known as the "Valle de Viñales," which is renowned for its dramatic limestone formations, known as "mogotes." The region is also home to the Zapata Swamp, a unique ecosystem that supports a wide variety of wildlife.
- The Central Region: This region is dominated by the Sierra Maestra, a mountain range that stretches for over 100 miles. This mountainous region is home to numerous waterfalls, caves, and forests, and is a popular destination for hiking and adventure tourism.
- The Eastern Region: The eastern region is characterized by a more rugged coastline, with numerous bays, inlets, and beaches. The terrain is also more varied, with rolling hills and valleys.
Comparing the Maps: Key Differences and Similarities
While both Puerto Rico and Cuba share a Caribbean location, their maps reveal key differences that have shaped their histories and cultures.
- Size and Shape: Cuba is significantly larger than Puerto Rico, with a more elongated shape. This difference in size and shape has influenced their economic development and cultural identity.
- Terrain: Both islands feature mountainous regions, but Cuba’s Sierra Maestra is significantly larger and more rugged than Puerto Rico’s Cordillera Central. This difference in terrain has impacted their agricultural potential and transportation infrastructure.
- Coastal Features: Both islands have diverse coastlines, but Cuba’s coastline is longer and more indented, offering a greater variety of beaches, bays, and inlets. This difference has influenced their tourism industry and maritime trade.
The Importance of Understanding the Maps
Beyond their geographical features, the maps of Puerto Rico and Cuba offer valuable insights into their historical and cultural development.
- Historical Significance: The maps reveal key geographical features that have influenced historical events, such as the location of settlements, the routes of exploration, and the sites of battles.
- Cultural Identity: The maps reflect the diverse landscapes and ecosystems that have shaped the cultures of these islands, influencing their food, music, and art.
- Economic Development: The maps provide insights into the natural resources and infrastructure that have influenced their economic development, such as agriculture, tourism, and trade.
FAQs: Exploring the Maps in More Detail
Q: What are the major cities located on the maps of Puerto Rico and Cuba?
A: Puerto Rico’s major cities include San Juan, Ponce, and Mayagüez, while Cuba’s major cities include Havana, Santiago de Cuba, and Camagüey.
Q: What are the major agricultural products grown in Puerto Rico and Cuba?
A: Both islands are known for their agricultural production, with Puerto Rico specializing in coffee, sugar cane, and fruits, while Cuba is known for tobacco, sugar cane, and citrus fruits.
Q: What are the major tourist attractions located on the maps of Puerto Rico and Cuba?
A: Puerto Rico boasts attractions like Old San Juan, El Yunque National Forest, and the bioluminescent bay, while Cuba is known for its colonial cities, beautiful beaches, and vibrant culture.
Q: What are the major transportation routes on the maps of Puerto Rico and Cuba?
A: Both islands have well-developed road networks, with Puerto Rico relying heavily on highways, while Cuba features a combination of highways and rural roads.
Tips for Navigating the Maps
- Use a reliable online map service: Websites like Google Maps and Bing Maps offer detailed maps of Puerto Rico and Cuba, with information on roads, cities, and attractions.
- Focus on key geographical features: Pay attention to the major mountains, rivers, and coastlines to understand the island’s topography and how it has influenced its development.
- Explore the historical context: Research historical events and settlements to gain a deeper understanding of the islands’ past and how it has shaped their present.
- Consider the cultural landscape: Look for cultural landmarks, festivals, and traditions to appreciate the unique cultural identity of each island.
Conclusion: A Journey Through the Caribbean
The maps of Puerto Rico and Cuba provide a window into the diverse landscapes, rich histories, and vibrant cultures of these Caribbean islands. By understanding their geographical features, historical context, and cultural identity, we gain a deeper appreciation for the unique contributions they make to the Caribbean mosaic. Whether exploring the bustling cities, the rugged mountains, or the pristine beaches, these islands offer a journey through time and culture, leaving a lasting impression on all who visit.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Caribbean: A Comparative Look at the Maps of Puerto Rico and Cuba. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!