Navigating Time: Understanding the Map of United States Time Zones
Related Articles: Navigating Time: Understanding the Map of United States Time Zones
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Time: Understanding the Map of United States Time Zones. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Time: Understanding the Map of United States Time Zones
The United States, a vast and geographically diverse nation, spans multiple time zones, creating a complex system for coordinating schedules and communication. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the map of United States time zones, delving into its history, intricacies, and practical implications.
A Glimpse into History: The Evolution of Time Zones
Prior to the late 19th century, each town and city in the United States operated on its own "local time," determined by the position of the sun. This led to significant inconsistencies and logistical challenges, particularly for railroads and other industries requiring synchronized operations.
In 1883, the United States adopted four standard time zones: Eastern, Central, Mountain, and Pacific. This standardization, driven by the need for efficient transportation and communication, resulted in a more cohesive timekeeping system.
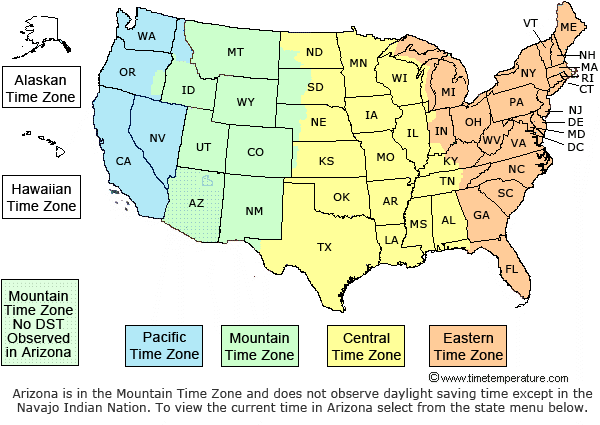
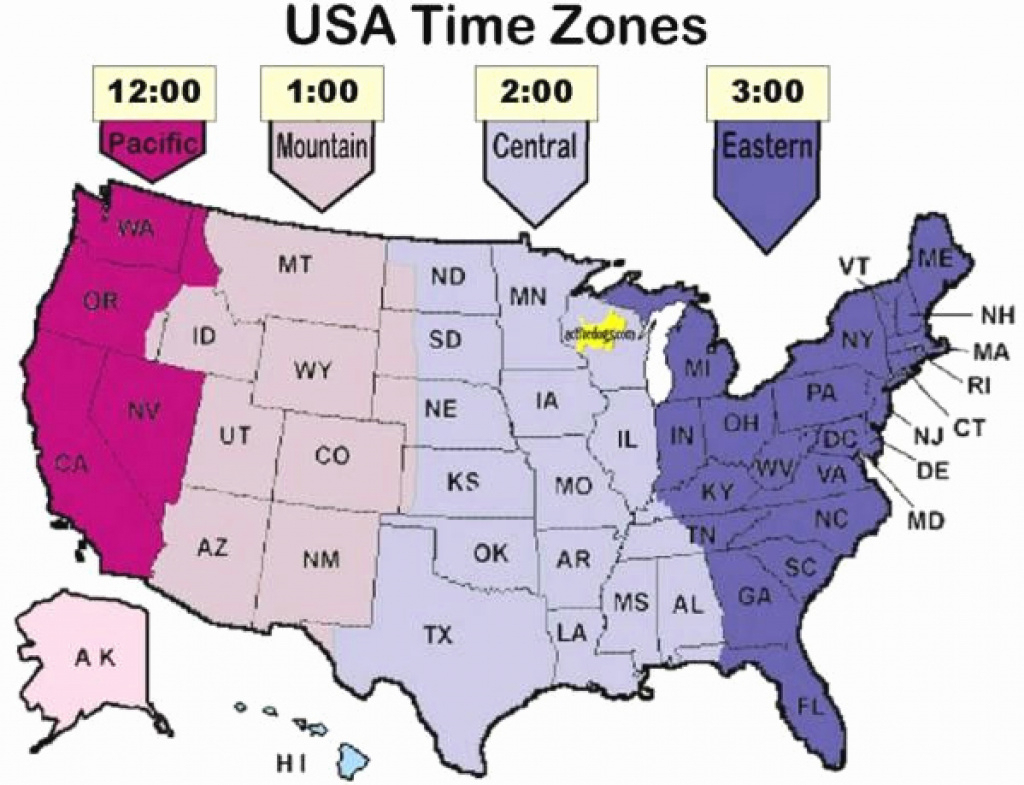
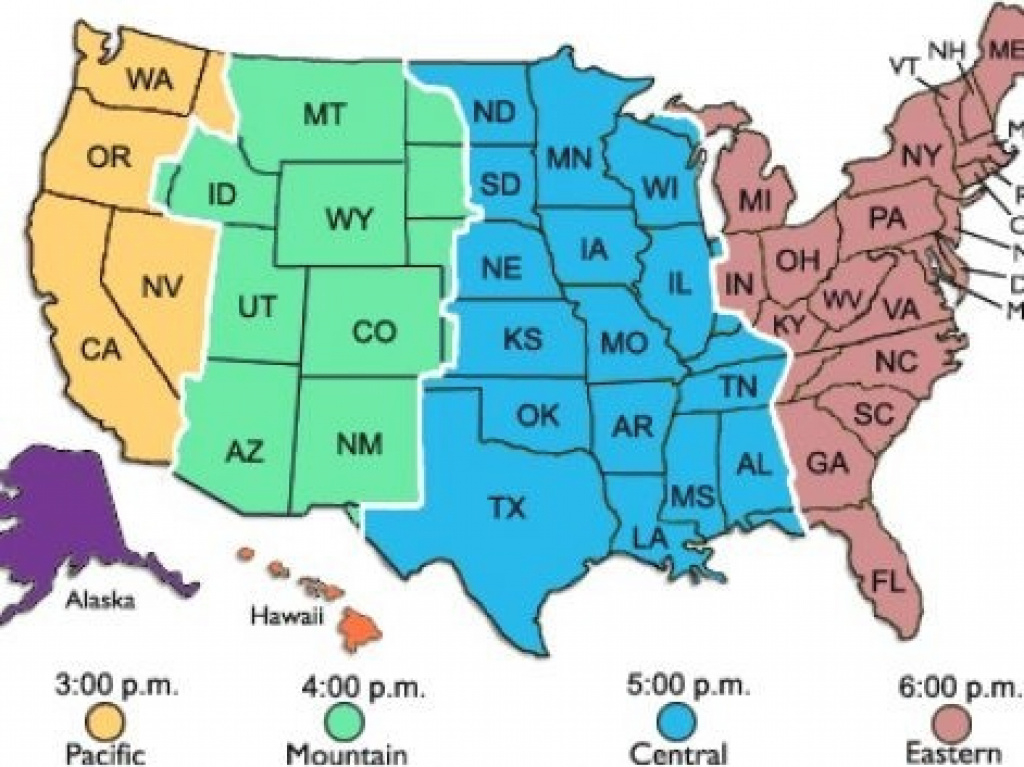
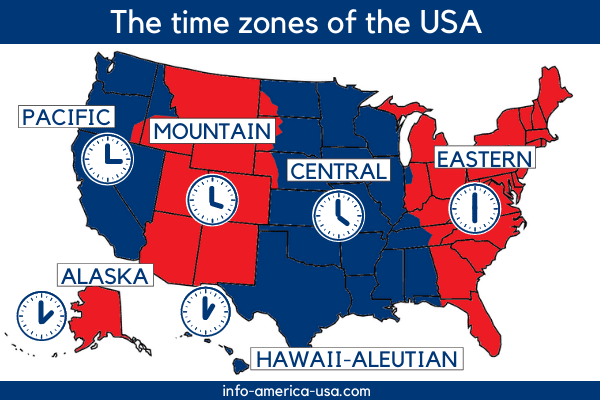
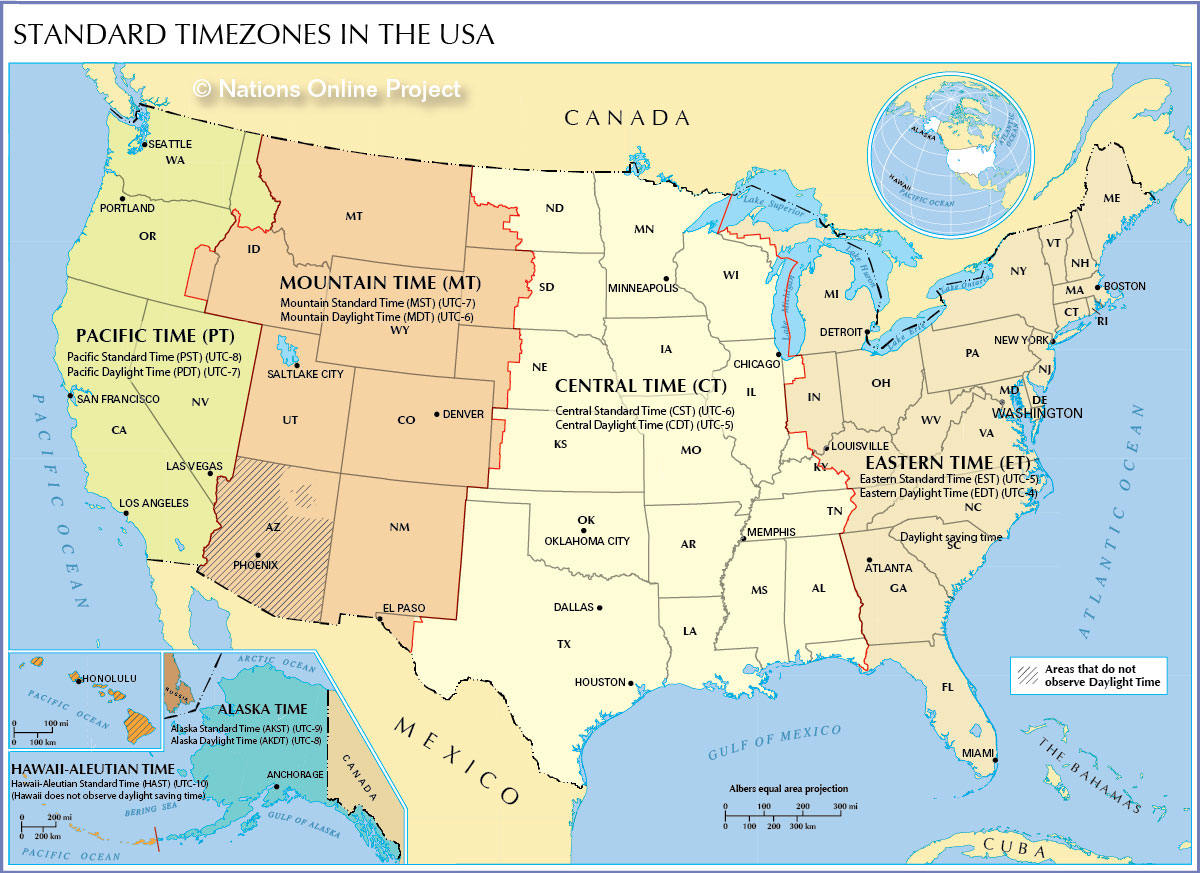
The Map of United States Time Zones: A Visual Representation
The map of United States time zones visually depicts the geographic division of the country into four primary time zones, each offset from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) by a specific number of hours:
- Eastern Time (ET): GMT -5 hours. Covers the eastern portion of the United States, including major cities like New York City, Boston, Philadelphia, and Miami.
- Central Time (CT): GMT -6 hours. Encompasses the central part of the country, including cities like Chicago, Dallas, Houston, and New Orleans.
- Mountain Time (MT): GMT -7 hours. Covers the western region, including cities like Denver, Phoenix, Salt Lake City, and Albuquerque.
- Pacific Time (PT): GMT -8 hours. Includes the westernmost states, including Los Angeles, San Francisco, Seattle, and Portland.
Beyond the Four: The Intricacies of Time Zones
While the four primary time zones form the core of the US timekeeping system, several nuances and exceptions add complexity:
- Alaska Time (AKT): GMT -9 hours. Located in the state of Alaska, it is an hour behind Pacific Time.
- Hawaii-Aleutian Standard Time (HST): GMT -10 hours. Applicable to the state of Hawaii and some islands in the Aleutian chain, it is two hours behind Pacific Time.
- Daylight Saving Time (DST): During the summer months, most of the United States, excluding Arizona and Hawaii, observe Daylight Saving Time, shifting their clocks forward by one hour. This practice, aimed at maximizing daylight hours during summer, introduces a fifth, temporary time zone.
The Importance of Understanding Time Zones
The map of United States time zones is crucial for various reasons:
- Efficient Communication: It enables individuals and businesses to coordinate schedules and meetings across different locations, ensuring timely communication and collaboration.
- Transportation and Travel: Understanding time zones is essential for travelers, allowing them to plan itineraries, book flights, and adjust to different time zones effectively.
- Business Operations: Businesses with operations in multiple time zones need to be cognizant of time differences to optimize communication, scheduling, and logistics.
- Financial Markets: Time zones play a significant role in global financial markets, influencing trading hours and market movements.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about Time Zones
Q: Why are there time zones?
A: Time zones were introduced to standardize timekeeping across vast geographical areas, eliminating the inconsistencies and logistical challenges associated with "local time."
Q: How do I know which time zone I’m in?
A: You can determine your time zone using an online map of United States time zones, consulting a time zone converter, or checking your phone’s settings.
Q: What are the benefits of Daylight Saving Time?
A: Daylight Saving Time aims to maximize daylight hours during summer months, potentially reducing energy consumption and promoting outdoor activities.
Q: Are there any exceptions to Daylight Saving Time?
A: Arizona and Hawaii do not observe Daylight Saving Time, maintaining their standard time throughout the year.
Tips for Navigating Time Zones
- Use online time zone converters: These tools allow you to quickly convert times between different time zones.
- Set your phone’s time zone: Ensure your phone’s time zone is set to the correct location.
- Plan ahead for travel: When traveling across time zones, adjust your schedule and sleep patterns to minimize jet lag.
- Be mindful of business hours: When communicating with individuals or businesses in different time zones, consider their working hours.
Conclusion: Navigating Time with Precision
The map of United States time zones provides a visual framework for understanding the complex system of timekeeping across the country. By recognizing the intricacies of time zones, individuals and businesses can optimize communication, transportation, and business operations, ensuring efficiency and coordination in a geographically diverse nation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Time: Understanding the Map of United States Time Zones. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!