The Complex Tapestry of Iraq: A Look at its Ethnic Map
Related Articles: The Complex Tapestry of Iraq: A Look at its Ethnic Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Complex Tapestry of Iraq: A Look at its Ethnic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Tapestry of Iraq: A Look at its Ethnic Map
![[OS] Ethnic composition of Iraq [3837×3868] : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/gD-YBJe9_wsjbaG8Xagxw1hofu5y_PnFwylueevkn2U.png?auto=webpu0026s=b3ed849f205827ee96e36029d7daad8ac6a62932)
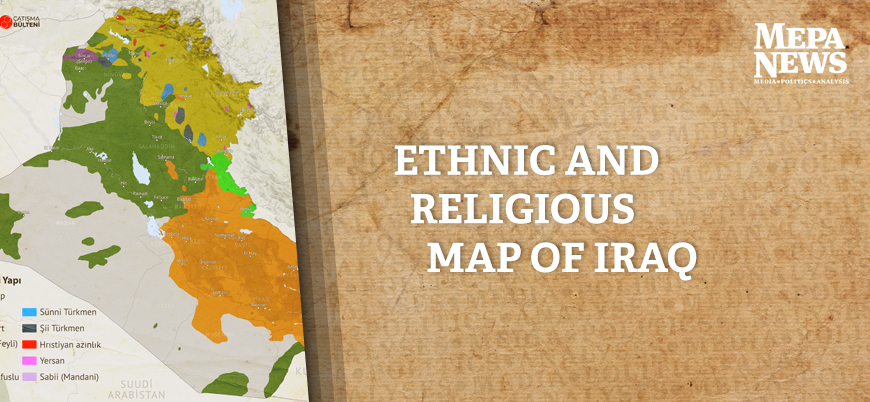
Iraq, a nation steeped in history and located in the heart of the Middle East, is a melting pot of diverse ethnicities and cultures. Understanding the ethnic composition of Iraq is crucial for grasping its historical evolution, contemporary dynamics, and future prospects. This article delves into the complexities of the Iraqi ethnic map, examining its key components and highlighting its significance in shaping the nation’s identity and trajectory.
A Multifaceted Mosaic:
The ethnic landscape of Iraq is a complex tapestry woven from various threads. The dominant ethnic groups include:
- Arabs: The largest ethnic group in Iraq, comprising approximately 75-80% of the population. Arab communities are further subdivided based on their tribal affiliations, historical origins, and regional identities.
- Kurds: The second-largest ethnic group, accounting for roughly 15-20% of the population. Kurds are primarily concentrated in the northern and northeastern regions of Iraq, with a strong sense of cultural and national identity.
- Turkmen: A Turkic ethnic group primarily located in the northern and western parts of Iraq. They constitute around 2-3% of the population and have a distinct language and cultural heritage.
- Other Minorities: Iraq is also home to several other minority groups, including Assyrians, Chaldeans, Armenians, Yazidis, and Shabaks, each contributing to the country’s rich cultural diversity.
The Historical Context:
The current ethnic map of Iraq is a product of centuries of historical events, migrations, and political developments. The region has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, including the Akkadian, Babylonian, Assyrian, Persian, Greek, Roman, Arab, Ottoman, and British empires, each leaving its mark on the cultural and ethnic fabric of the land.
- Ancient Mesopotamia: The cradle of civilization, Mesopotamia, witnessed the emergence of various civilizations, including the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. These ancient civilizations laid the foundation for the cultural and linguistic diversity that exists in Iraq today.
- Arab Conquests: The Arab conquests of the 7th century CE brought about a significant shift in the region’s demographics, leading to the widespread adoption of Arabic language and Islamic religion. This period also witnessed the emergence of new tribal identities and affiliations.
- Ottoman Rule: The Ottoman Empire ruled Iraq for centuries, integrating the region into its vast empire. The Ottoman period saw the influx of Turkmen and other Turkic groups, further contributing to the ethnic mosaic of Iraq.
- British Mandate: After World War I, Iraq was placed under British control as a mandate territory. The British administration played a significant role in shaping the modern boundaries of Iraq, which included a diverse range of ethnic groups.
- Post-Independence: Following independence in 1932, Iraq faced various challenges, including ethnic tensions and conflicts. The Ba’athist regime, which ruled Iraq from 1968 to 2003, attempted to suppress ethnic identities and promote a unified Arab national identity.
The Ethnic Map and its Significance:
The ethnic map of Iraq is not merely a geographical representation of population distribution. It holds profound implications for understanding the country’s political, social, and cultural landscape.
- Political Dynamics: Ethnic identities have played a significant role in Iraqi politics. The struggle for power and resources has often been shaped by ethnic allegiances and grievances. The Kurdish quest for autonomy, the Turkmen desire for representation, and the Assyrians’ concerns over cultural preservation are just a few examples of how ethnic identities have impacted political dynamics.
- Social Cohesion: The diverse ethnic composition of Iraq has both fostered social cohesion and contributed to tensions. Inter-ethnic relations have been marked by periods of cooperation and conflict, with historical grievances, cultural differences, and economic disparities often fueling tensions.
- Cultural Heritage: Iraq’s rich cultural heritage is a product of its diverse ethnicities. Each ethnic group contributes its unique traditions, languages, art forms, and beliefs to the nation’s cultural tapestry. The preservation and promotion of this cultural diversity are crucial for maintaining the vibrancy of Iraqi society.
- Security and Stability: Ethnic tensions and conflicts have posed significant challenges to Iraq’s security and stability. The country has witnessed numerous instances of sectarian violence, ethnic cleansing, and armed conflict, highlighting the importance of addressing ethnic grievances and promoting inter-ethnic dialogue.
The Future of Iraq’s Ethnic Map:
The future of Iraq’s ethnic map remains uncertain. The country faces numerous challenges, including political instability, sectarian violence, economic hardship, and the threat of terrorism. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that recognizes the importance of ethnic diversity, promotes inter-ethnic dialogue and reconciliation, and ensures the equal rights and representation of all ethnic groups.
FAQs about the Ethnic Map of Iraq:
Q: What is the most dominant ethnic group in Iraq?
A: The most dominant ethnic group in Iraq is the Arabs, accounting for approximately 75-80% of the population.
Q: Where are the Kurds primarily located in Iraq?
A: The Kurds are primarily concentrated in the northern and northeastern regions of Iraq, with a strong sense of cultural and national identity.
Q: What is the role of the Turkmen in Iraqi society?
A: The Turkmen, a Turkic ethnic group, are primarily located in the northern and western parts of Iraq. They constitute around 2-3% of the population and have a distinct language and cultural heritage.
Q: How has the historical context shaped the ethnic map of Iraq?
A: The current ethnic map of Iraq is a product of centuries of historical events, migrations, and political developments, including the rise and fall of empires, conquests, and administrative changes.
Q: What are the implications of the ethnic map for Iraqi politics?
A: Ethnic identities have played a significant role in Iraqi politics, often shaping the struggle for power and resources.
Q: What are the challenges facing Iraq in terms of ethnic relations?
A: Iraq faces numerous challenges related to ethnic relations, including historical grievances, cultural differences, economic disparities, and the potential for sectarian violence and conflict.
Tips for Understanding the Ethnic Map of Iraq:
- Consult reliable sources: Refer to reputable academic publications, government reports, and international organizations for accurate and up-to-date information on the ethnic map of Iraq.
- Engage in critical thinking: Analyze information from multiple perspectives and consider the potential biases and limitations of different sources.
- Be aware of cultural sensitivities: Respect the cultural and religious diversity of Iraq and avoid making generalizations or stereotypes about specific ethnic groups.
- Promote understanding and dialogue: Encourage open and respectful discussions about the ethnic complexities of Iraq and the challenges of promoting inter-ethnic harmony.
Conclusion:
The ethnic map of Iraq is a complex and dynamic landscape that reflects the country’s rich history, diverse cultures, and ongoing challenges. Understanding the ethnic composition of Iraq is crucial for grasping its historical evolution, contemporary dynamics, and future prospects. By promoting inter-ethnic dialogue, fostering inclusivity, and addressing the root causes of ethnic tensions, Iraq can strive towards a more peaceful and prosperous future that embraces its diverse heritage and builds a society based on shared values and common aspirations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Tapestry of Iraq: A Look at its Ethnic Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!