The Dniester River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography
Related Articles: The Dniester River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Dniester River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Dniester River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography

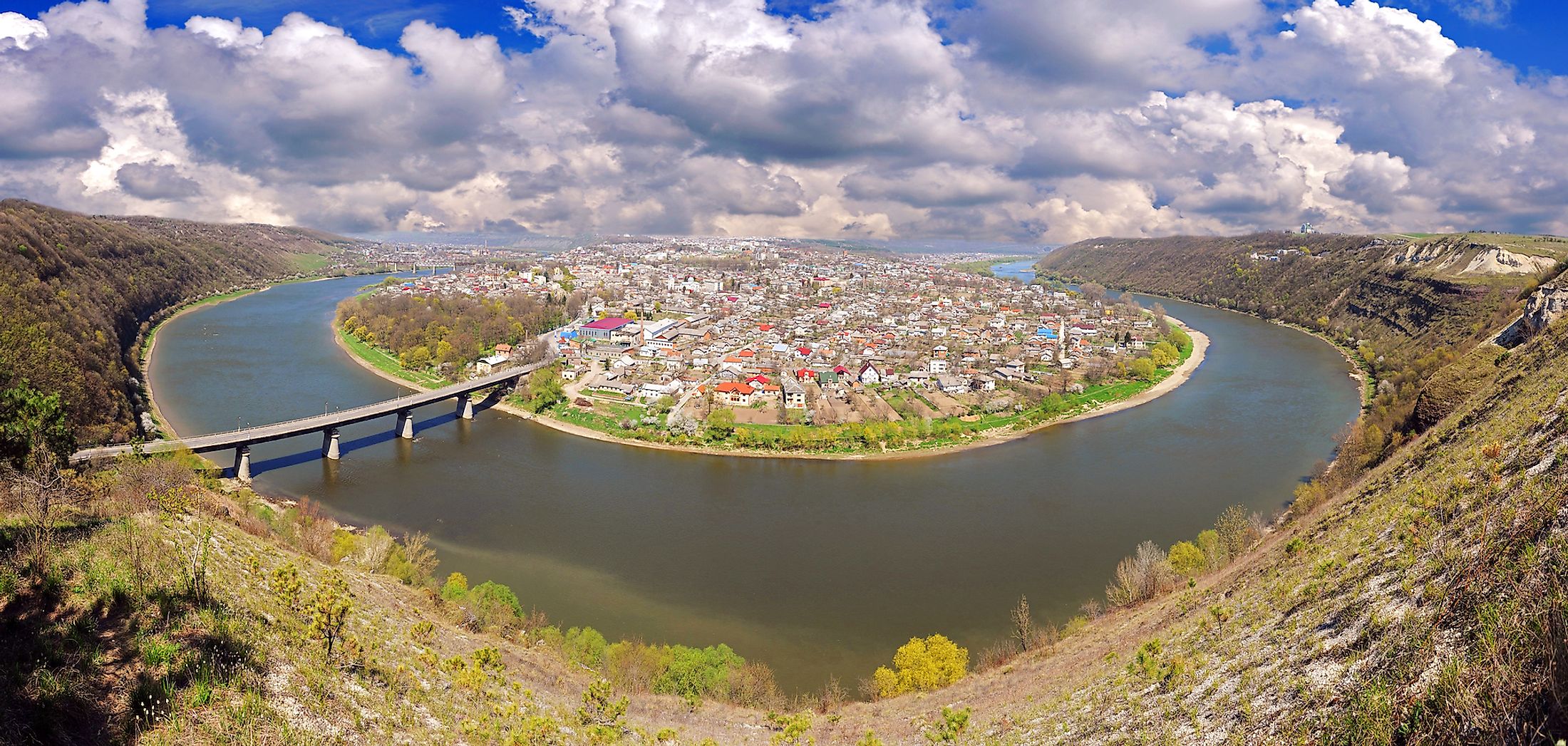
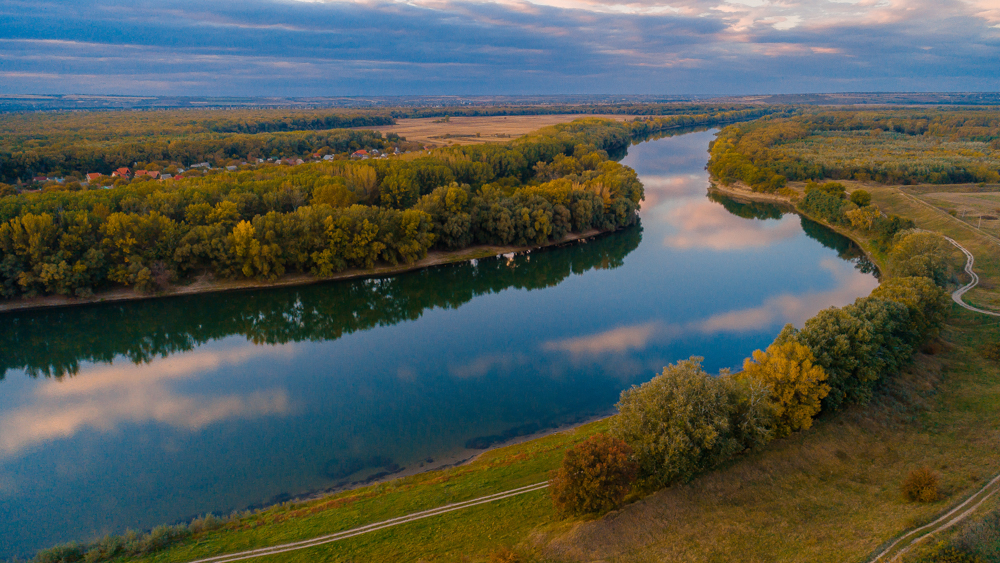
The Dniester River, a significant waterway flowing through Eastern Europe, holds a rich history and a vital role in the region’s geography, culture, and economy. Its winding path, stretching over 1,352 kilometers (840 miles), carves a unique landscape, influencing the lives of millions who reside along its banks.
A Journey Through Time and Terrain:
Originating in the Carpathian Mountains of Ukraine, the Dniester River flows eastward, forming a natural border between Ukraine and Moldova before emptying into the Black Sea. Its journey is marked by a diverse terrain, traversing through rolling hills, fertile valleys, and rugged gorges. This variation in topography contributes to the river’s unique character and its influence on the surrounding environment.
A Tapestry of History:
The Dniester River has witnessed centuries of human activity, leaving behind a rich tapestry of history. Ancient civilizations, including the Scythians and Greeks, established settlements along its banks, utilizing the river for trade, transportation, and irrigation. The river’s strategic location, bordering diverse cultures and empires, has often made it a focal point of conflict and territorial disputes.
Economic Significance and Environmental Impact:
The Dniester River continues to play a vital role in the economies of the countries it traverses. Its waters are used for irrigation, hydropower generation, and fishing. The river’s fertile valley provides suitable land for agriculture, supporting a significant agricultural sector. However, the river’s economic importance comes with environmental challenges. Industrial pollution, agricultural runoff, and over-exploitation of water resources threaten the river’s ecological balance.
Cultural Significance and Tourism:
The Dniester River is not merely a geographical feature; it is deeply intertwined with the cultural identity of the region. Its banks are dotted with ancient monasteries, historic castles, and traditional villages, each bearing witness to the river’s influence on local traditions and folklore. The river’s natural beauty, coupled with its rich cultural heritage, attracts tourists from across the globe, contributing to the region’s tourism industry.
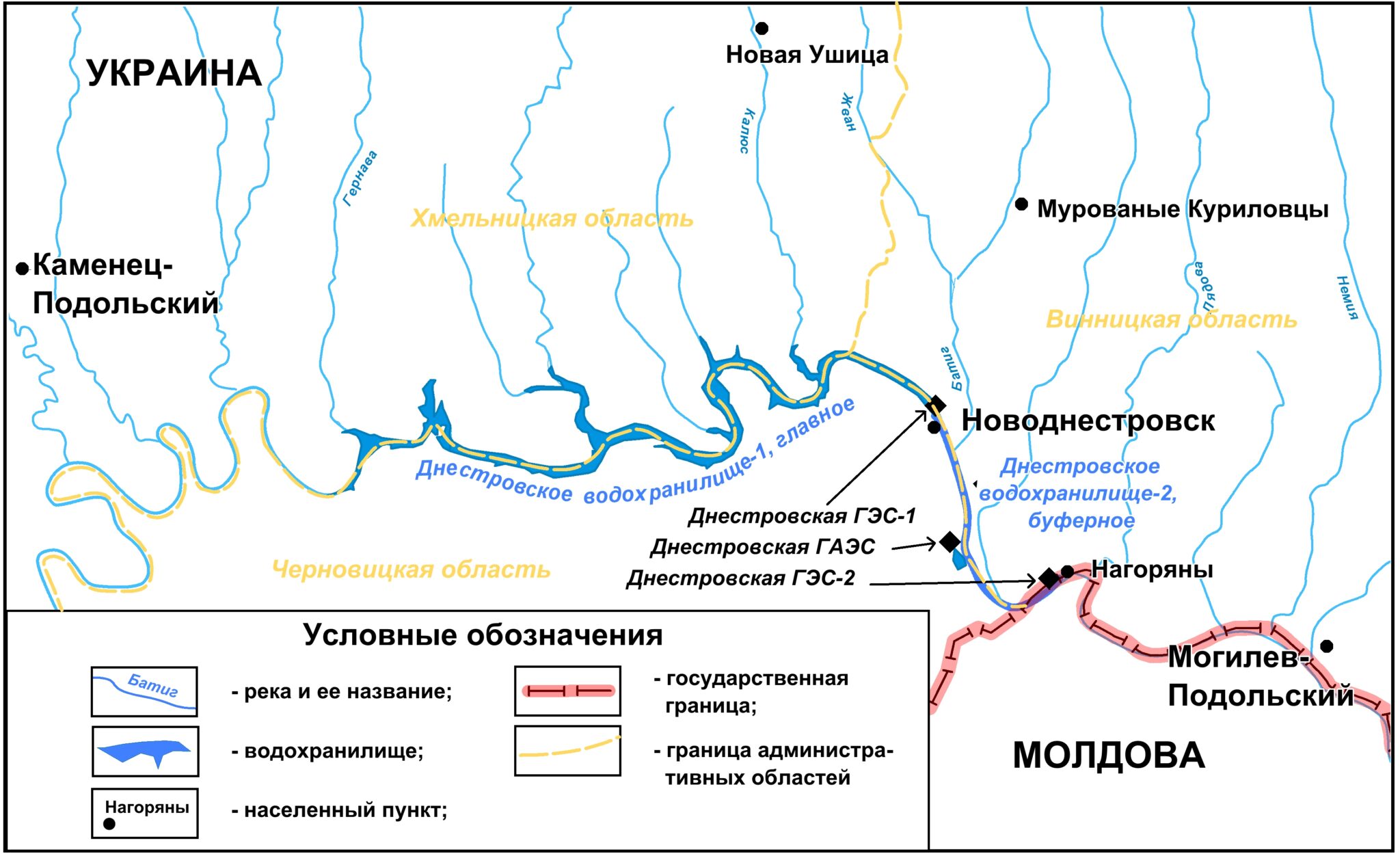
Exploring the Dniester River on a Map:
To fully comprehend the significance of the Dniester River, it is crucial to visualize its path on a map. Here are key geographical features to consider:
- Source: The river’s origin lies in the Carpathian Mountains of Ukraine, specifically near the town of Turka.
- Course: The Dniester flows eastward, forming a natural border between Ukraine and Moldova for a significant portion of its course.
- Mouth: The river empties into the Black Sea near the city of Ovidiopol in Ukraine.
- Major Cities: Important cities located along the Dniester River include Chernivtsi, Khmelnytskyi, and Ternopil in Ukraine, as well as Tiraspol and Bender in Moldova.
- Tributaries: The Dniester River is fed by numerous tributaries, including the Stryi, Zbruch, and Seret rivers.
Understanding the Dniester River’s Impact:
By examining the Dniester River’s course on a map, one can better understand its impact on the surrounding landscape and human activity. The river’s meandering path creates fertile valleys, ideal for agriculture, while its steep banks provide natural barriers for defense and settlement. The river’s presence has shaped the region’s cultural heritage, influencing local traditions, folklore, and architectural styles.
A River Facing Challenges:
Despite its historical and economic significance, the Dniester River faces various challenges. Pollution from industrial activities and agricultural runoff threaten the river’s ecosystem. Over-exploitation of water resources for irrigation and hydropower generation has led to concerns about water scarcity and ecological imbalances.
Protecting the Dniester River:
Efforts are underway to protect the Dniester River and its surrounding environment. International cooperation between Ukraine and Moldova is crucial to address transboundary pollution and implement sustainable water management practices. Conservation initiatives focus on restoring damaged ecosystems, promoting responsible fishing practices, and raising public awareness about the importance of protecting the river’s natural resources.
FAQs About the Dniester River:
Q: How long is the Dniester River?
A: The Dniester River is approximately 1,352 kilometers (840 miles) long.
Q: What countries does the Dniester River flow through?
A: The Dniester River flows through Ukraine and Moldova.
Q: What is the main economic activity associated with the Dniester River?
A: The Dniester River is vital for agriculture, hydropower generation, and fishing.
Q: What are some of the environmental challenges facing the Dniester River?
A: Pollution, agricultural runoff, and over-exploitation of water resources pose significant threats to the river’s ecosystem.
Q: What are some of the cultural landmarks associated with the Dniester River?
A: Ancient monasteries, historic castles, and traditional villages along the river’s banks reflect its rich cultural heritage.
Tips for Exploring the Dniester River:
- Visit historical sites: Explore ancient monasteries, castles, and traditional villages to immerse yourself in the region’s cultural heritage.
- Go fishing: The Dniester River is known for its diverse fish populations, offering anglers a unique experience.
- Enjoy scenic boat tours: Take a boat trip along the river to appreciate its natural beauty and diverse landscapes.
- Learn about local traditions: Engage with local communities to learn about their unique customs and folklore.
- Support sustainable tourism: Choose eco-friendly accommodations and activities to minimize your environmental impact.
Conclusion:
The Dniester River, a lifeline through history and geography, continues to play a vital role in the lives of millions who reside along its banks. Its winding path, rich history, and diverse ecosystem make it a fascinating subject of study and a captivating destination for travelers. Understanding the river’s importance and addressing the challenges it faces is crucial for ensuring its continued significance for future generations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Dniester River: A Lifeline Through History and Geography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!