The Illinois Gerrymandering Map: A Case Study in Political Manipulation
Related Articles: The Illinois Gerrymandering Map: A Case Study in Political Manipulation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Illinois Gerrymandering Map: A Case Study in Political Manipulation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Illinois Gerrymandering Map: A Case Study in Political Manipulation
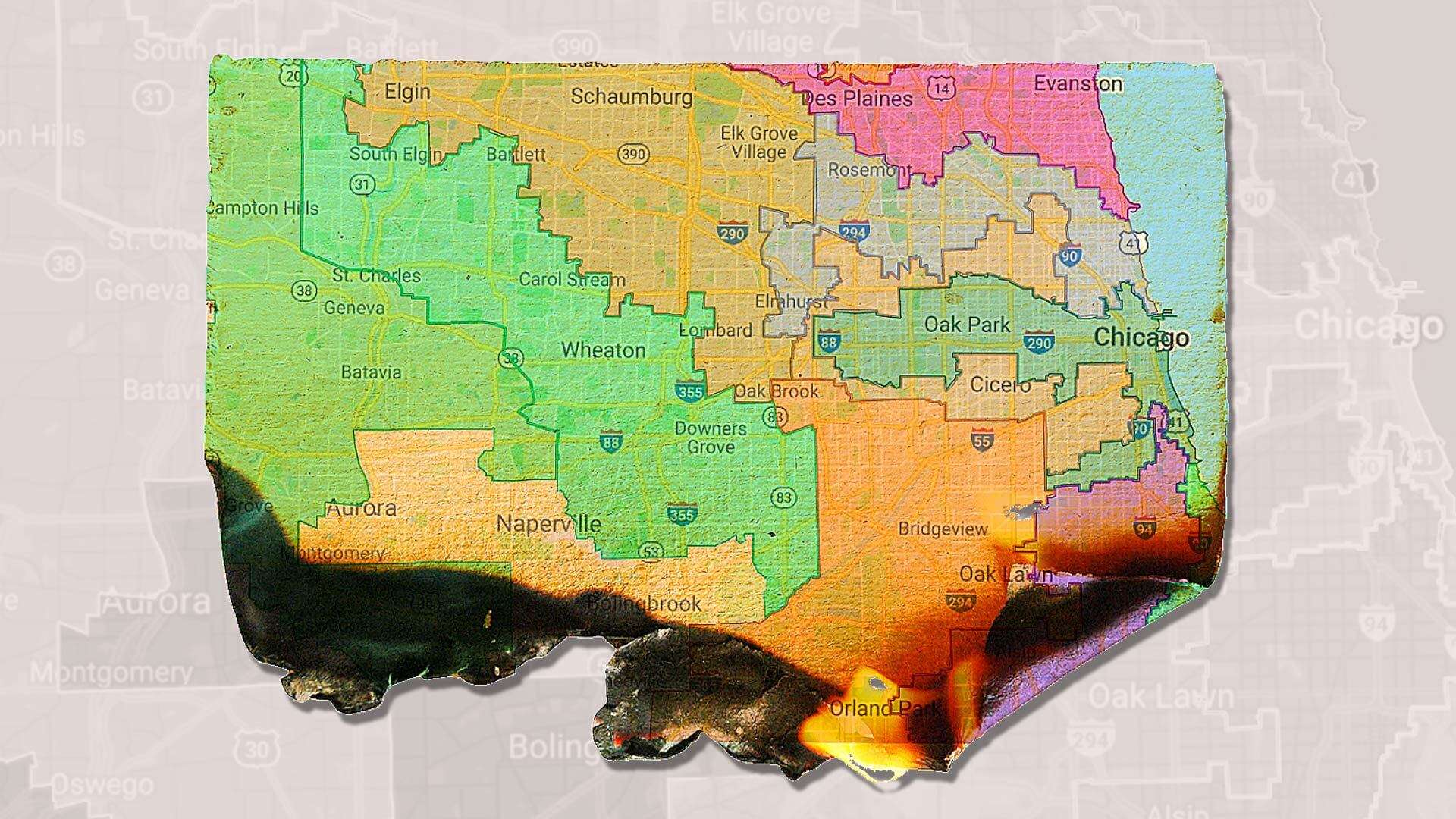
The Illinois gerrymandering map, a product of the 2010 redistricting process, stands as a stark example of how political boundaries can be manipulated to achieve partisan advantage. This map, with its contorted districts resembling bizarre creatures rather than cohesive communities, has become a symbol of the deeply entrenched issue of gerrymandering in American politics.
Understanding the Mechanics of Gerrymandering
Gerrymandering, the practice of manipulating electoral districts to favor a particular party or group, has a long and complex history. It derives its name from Elbridge Gerry, the governor of Massachusetts in 1812, whose redistricting efforts created a district resembling a salamander, sparking accusations of political manipulation.
The core principle of gerrymandering lies in the strategic manipulation of district boundaries to concentrate opposing voters in a limited number of districts, while spreading the supporting voters thinly across multiple districts. This can lead to situations where a party can win a majority of seats in a legislature while receiving a minority of votes statewide.
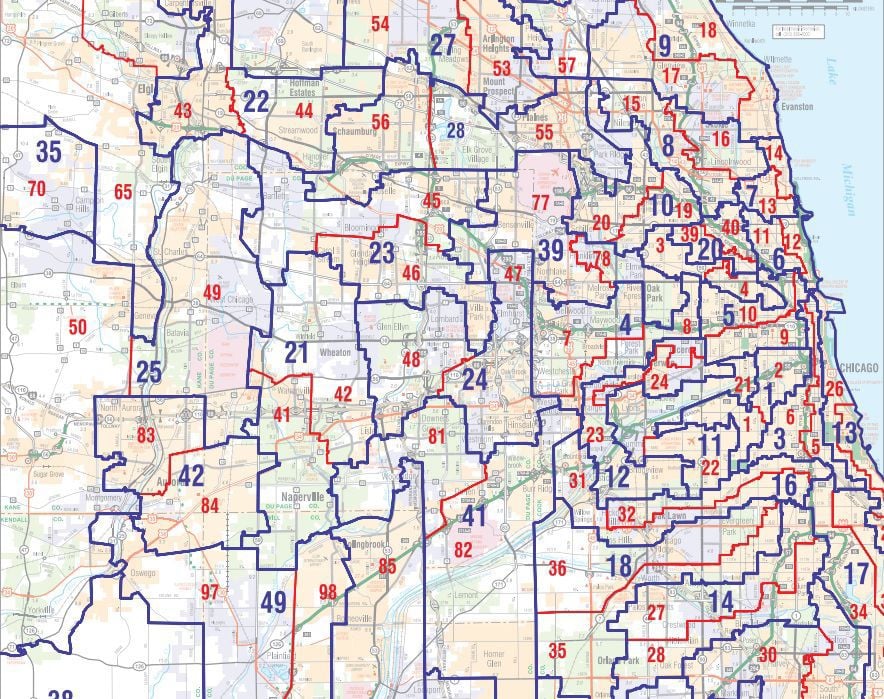
The Illinois Map: A Case Study in Partisan Gerrymandering
The 2010 redistricting process in Illinois, conducted by a Democratic-controlled legislature, led to the creation of a map heavily criticized for its partisan bias. The map resulted in a significant advantage for Democrats in state elections, with critics arguing that it diluted the voting power of Republicans and independents.
Key Features of the Illinois Gerrymandering Map:
- Cracking: The map employed "cracking" tactics, dividing communities of opposing voters to ensure they couldn’t elect representatives. For example, Republican voters in suburban areas were split across multiple districts, diluting their collective voting power.
- Packing: "Packing" involved concentrating opposing voters into a limited number of districts, ensuring they could only win a few seats. This tactic was applied to Republican voters in rural areas, effectively limiting their representation.
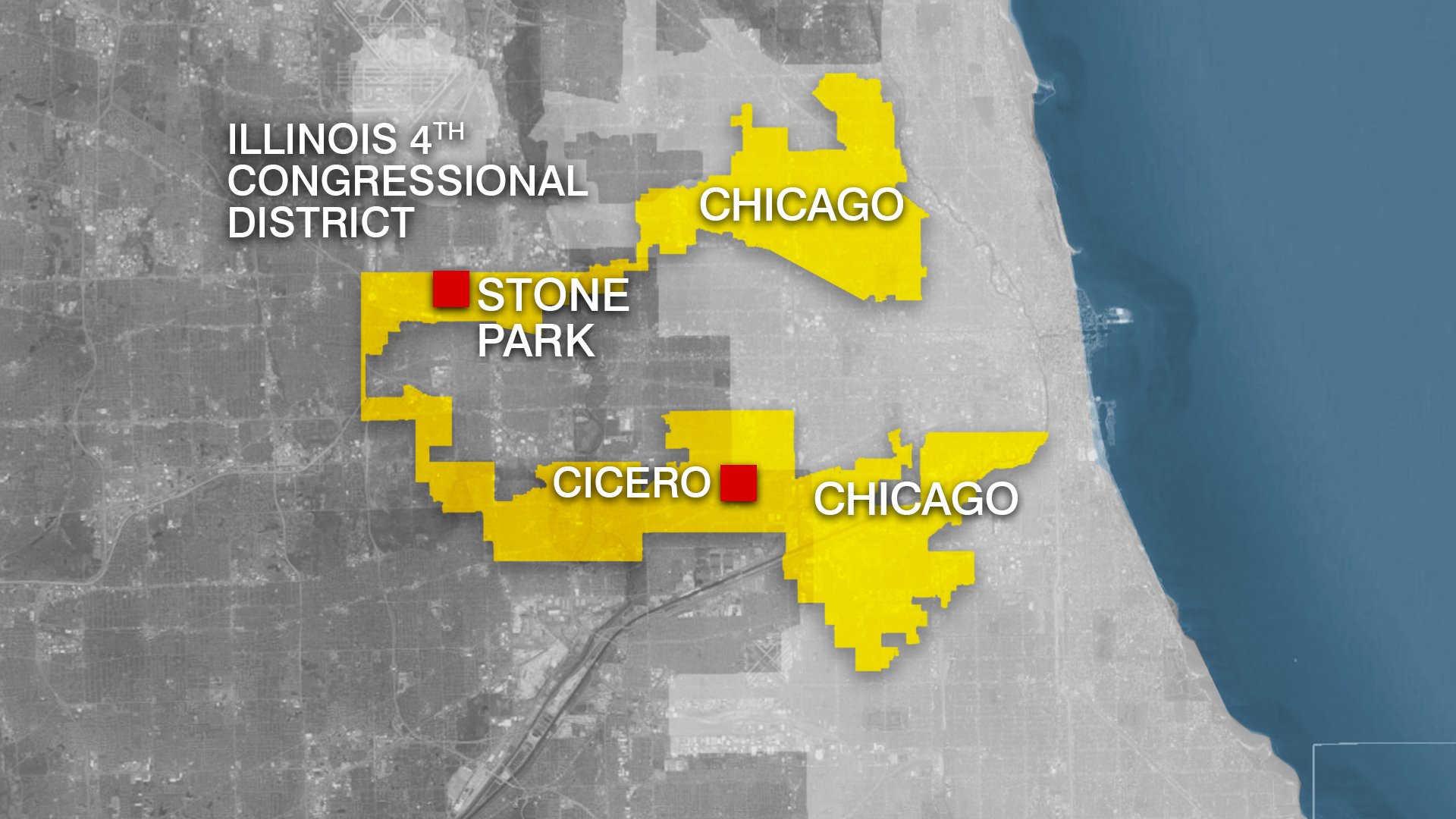
- Unnatural Boundaries: The map featured bizarre district lines that ignored natural boundaries and community cohesiveness, often splitting neighborhoods and cities. This manipulation was evident in districts that resembled long, thin strips stretching across multiple counties, creating a sense of artificiality and disenfranchisement.
The Consequences of Gerrymandering in Illinois:
The Illinois gerrymandering map has had a significant impact on state politics:
- Reduced Competition: The map has created a system where incumbents enjoy a significant advantage, discouraging competitive elections and reducing voter engagement.
- Polarization: Gerrymandering contributes to political polarization by creating safe districts for both parties, reducing incentives for compromise and bipartisanship.
- Underrepresentation: The map has resulted in the underrepresentation of certain groups, particularly Republicans and independents, undermining the principle of fair and equal representation.
The Fight Against Gerrymandering in Illinois
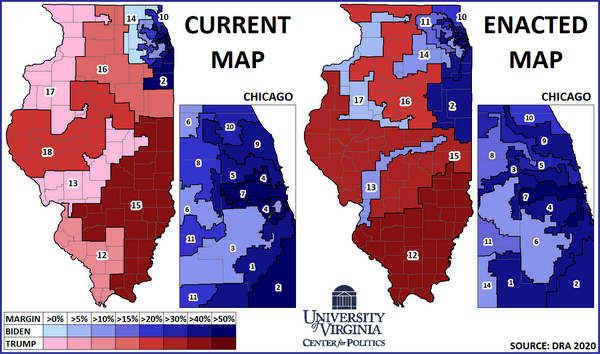
The Illinois gerrymandering map has sparked widespread criticism and legal challenges. In 2018, a federal court ruled that the map was unconstitutional, finding that it violated the Voting Rights Act and the First Amendment. The court ordered the state to redraw the map, leading to a new redistricting process in 2020.
The new map, while still subject to debate, represents a step towards fairer representation in Illinois. It features more competitive districts, reducing the influence of partisan gerrymandering.
FAQs on the Illinois Gerrymandering Map:
Q: What is the main purpose of gerrymandering?
A: The primary purpose of gerrymandering is to manipulate electoral districts to favor a particular party or group, ensuring their candidates win elections even if they receive a minority of votes statewide.
Q: How does the Illinois gerrymandering map affect voters?
A: The map has reduced competition in elections, making it harder for voters to choose between different candidates. It has also led to the underrepresentation of certain groups, particularly Republicans and independents, undermining the principle of fair and equal representation.
Q: What are the legal challenges to the Illinois gerrymandering map?
A: The map has been challenged in court on the grounds that it violates the Voting Rights Act and the First Amendment. The court ruled that the map was unconstitutional, leading to a new redistricting process.
Q: What are the potential solutions to address gerrymandering in Illinois?
A: Solutions include:
- Independent Redistricting Commissions: These commissions, composed of non-partisan individuals, can be tasked with drawing electoral districts, removing the influence of political parties.
- Fair Districting Standards: Establishing clear standards for drawing fair districts, such as compactness and contiguity, can help prevent manipulation.
- Public Participation: Encouraging public involvement in the redistricting process can ensure that diverse voices are heard and considered.
Tips for Understanding and Addressing Gerrymandering:
- Become Informed: Educate yourself about the issue of gerrymandering and how it affects your community.
- Advocate for Reform: Support organizations and initiatives working to reform redistricting processes.
- Engage in the Political Process: Participate in elections and advocate for candidates who support fair redistricting practices.
- Stay Informed: Follow news and developments related to redistricting and gerrymandering in your state.
Conclusion:
The Illinois gerrymandering map serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of political manipulation. It highlights the importance of fair and transparent redistricting processes that ensure equal representation for all voters. By understanding the mechanics of gerrymandering, its consequences, and the potential solutions, citizens can play a vital role in advocating for a more democratic and representative system. The fight against gerrymandering is an ongoing battle, but by working together, communities can strive towards a future where elections are fair and representative of the will of the people.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Illinois Gerrymandering Map: A Case Study in Political Manipulation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!