The Power of Abstraction: Understanding Generic Maps in Data Visualization
Related Articles: The Power of Abstraction: Understanding Generic Maps in Data Visualization
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Abstraction: Understanding Generic Maps in Data Visualization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Power of Abstraction: Understanding Generic Maps in Data Visualization
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Power of Abstraction: Understanding Generic Maps in Data Visualization
- 3.1 Defining the Essence of Generic Maps
- 3.2 Key Components of a Generic Map
- 3.3 Benefits of Using Generic Maps
- 3.4 Applications of Generic Maps
- 3.5 Generic Maps: A Foundation for Effective Data Visualization
- 3.6 FAQs about Generic Maps
- 3.7 Tips for Using Generic Maps Effectively
- 3.8 Conclusion: The Power of Abstraction in Data Visualization
- 4 Closure
The Power of Abstraction: Understanding Generic Maps in Data Visualization

In the realm of data visualization, where the goal is to communicate complex information clearly and effectively, the concept of a generic map emerges as a powerful tool. This abstract representation, devoid of specific data or context, serves as a blueprint for creating visually appealing and insightful visualizations. By focusing on the underlying structure and relationships within data, generic maps provide a framework for building tailored visualizations that cater to specific data sets and analytical needs.
Defining the Essence of Generic Maps
A generic map, in its purest form, is a visual template that outlines the fundamental elements of a visualization. It acts as a skeletal structure, emphasizing the relationships between data points, categories, and dimensions without being tied to any specific data. This abstract nature grants generic maps remarkable flexibility, enabling them to adapt to a wide range of data sets and analytical objectives.
Imagine a map without geographical coordinates or specific landmarks. This conceptual map, devoid of concrete details, represents a generic map. It focuses on the abstract relationships between locations, routes, and connections, providing a framework for understanding spatial relationships. Similarly, generic maps in data visualization establish a foundational structure for visualizing data, highlighting key relationships and patterns without being restricted by the specifics of the data itself.
Key Components of a Generic Map
Generic maps, despite their abstract nature, possess specific components that define their structure and functionality:
- Visual Elements: These represent the fundamental building blocks of the visualization, such as points, lines, bars, or areas. The choice of visual elements depends on the nature of the data and the intended message.
- Relationships: Generic maps define how these visual elements interact and relate to each other, conveying the underlying structure of the data. This could involve proximity, hierarchy, flow, or other visual connections.
- Dimensions: These represent the different aspects of the data being visualized, such as time, location, category, or value. Generic maps define how these dimensions are represented and interact within the visualization.
- Scale and Scope: Generic maps establish a visual framework for representing the range and scale of the data. This ensures that the visualization accurately reflects the magnitude and distribution of the data points.
Benefits of Using Generic Maps
The abstract nature of generic maps offers several advantages in data visualization:
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Generic maps can be easily adapted to different data sets and analytical needs, allowing for the creation of tailored visualizations that effectively communicate specific insights.
- Consistency and Clarity: By establishing a standardized framework, generic maps ensure consistency in the design and structure of visualizations, enhancing clarity and comprehension.
- Focus on Data Relationships: Generic maps emphasize the relationships between data points and dimensions, facilitating the identification of patterns and trends.
- Reduced Design Time: Using a generic map as a starting point streamlines the design process, reducing the time and effort required to create effective visualizations.
- Improved Collaboration: Generic maps provide a common language and visual framework for data visualization, facilitating collaboration between analysts, designers, and stakeholders.
Applications of Generic Maps
Generic maps find applications in various fields and contexts, including:
- Business Intelligence: Generic maps can be used to create dashboards and reports that visualize key performance indicators, trends, and customer behavior.
- Scientific Research: Researchers leverage generic maps to visualize complex data sets, identify patterns, and communicate findings effectively.
- Marketing and Advertising: Generic maps aid in creating compelling visualizations that showcase product features, customer demographics, and campaign performance.
- Education and Training: Generic maps can be used to illustrate concepts, relationships, and processes, enhancing learning and understanding.
Generic Maps: A Foundation for Effective Data Visualization
Generic maps, by providing a conceptual framework for data visualization, empower analysts and designers to create impactful and insightful visualizations. They enable a focus on data relationships and patterns, fostering a deeper understanding of the information being presented. Their adaptability and flexibility make them a powerful tool for communicating data effectively across various fields and applications.
FAQs about Generic Maps
1. What is the difference between a generic map and a data visualization?
A generic map is a blueprint or template for data visualization, while a data visualization is a concrete representation of specific data using a generic map as a framework.
2. Are generic maps limited to specific data types?
No, generic maps are designed to be adaptable to various data types, including numerical, categorical, and spatial data.
3. How can I create a generic map?
Generic maps can be created using various tools, including data visualization software, diagramming tools, or even pen and paper. The key is to focus on the abstract relationships and structure of the data.
4. What are some examples of generic map types?
Common generic map types include scatter plots, bar charts, line graphs, network diagrams, and treemaps.
5. Can I use generic maps for interactive visualizations?
Yes, generic maps can be used as a foundation for creating interactive visualizations that allow users to explore and analyze data dynamically.
Tips for Using Generic Maps Effectively
- Start with the Data: Begin by understanding the data you want to visualize, its structure, and the relationships between its elements.
- Define Your Objectives: Clearly define the message you want to convey and the insights you want to highlight.
- Choose the Right Visual Elements: Select visual elements that best represent the data and its relationships, considering the intended audience and the desired level of detail.
- Maintain Consistency: Ensure that the visual elements and relationships within the generic map are consistent with the overall design and purpose of the visualization.
- Test and Iterate: Create prototypes and test different variations of the generic map to ensure its effectiveness in communicating the desired insights.
Conclusion: The Power of Abstraction in Data Visualization
Generic maps represent a powerful abstraction technique that enhances the effectiveness of data visualization. By focusing on the underlying structure and relationships within data, generic maps provide a framework for creating tailored visualizations that cater to specific analytical needs and effectively communicate complex information. Their adaptability, consistency, and focus on data relationships make them an invaluable tool for analysts, designers, and stakeholders alike. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, generic maps will play an increasingly important role in making data accessible, insightful, and actionable.

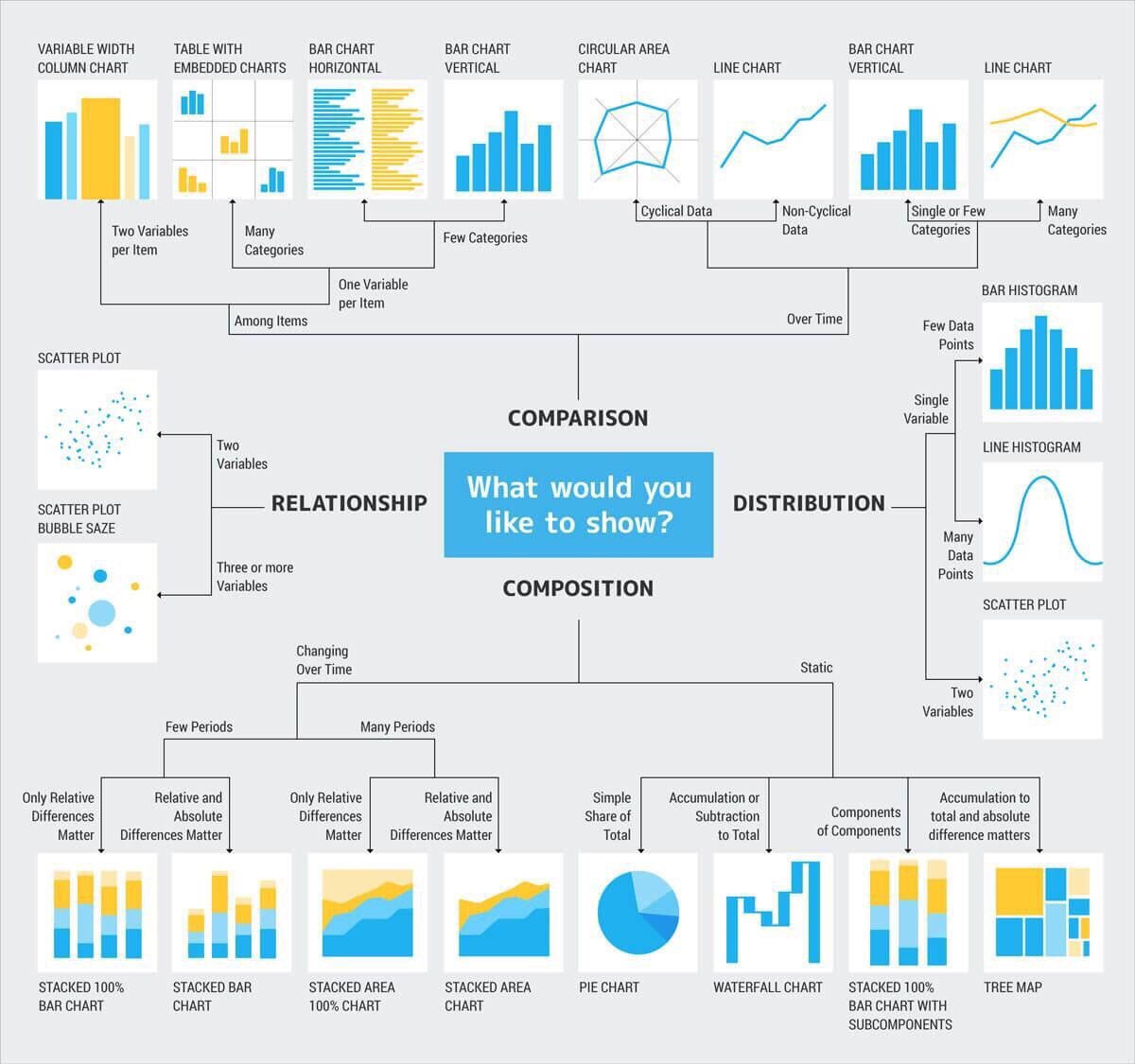


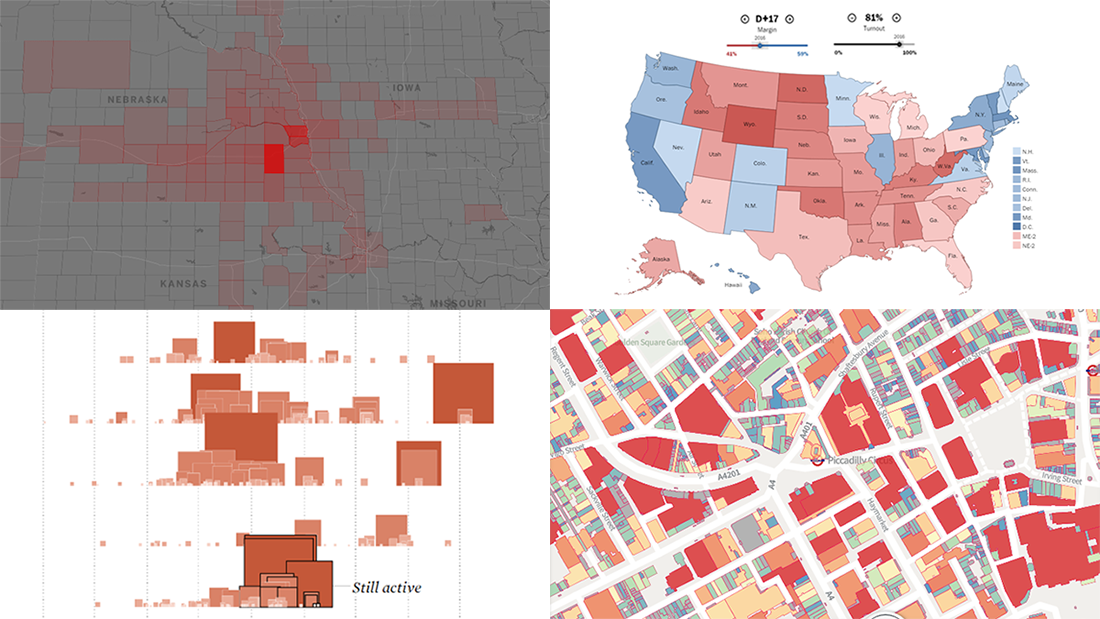

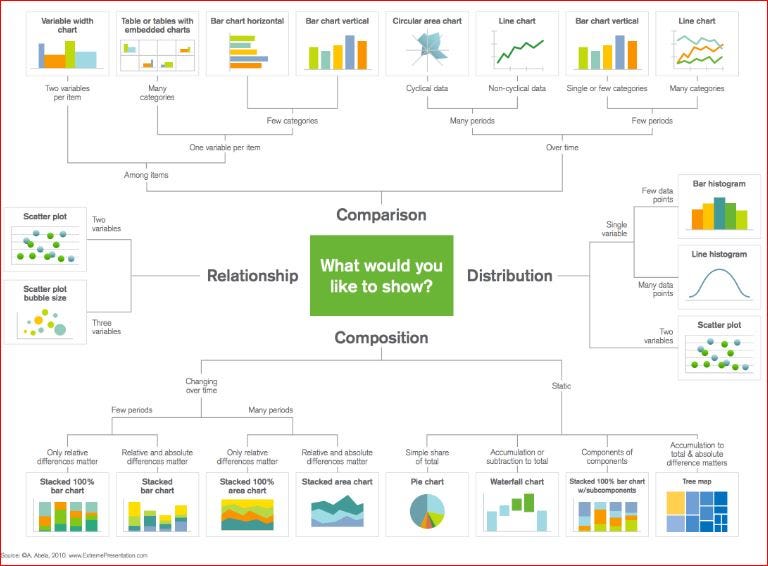
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Abstraction: Understanding Generic Maps in Data Visualization. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!