Unraveling the Autumnal Journey: A Look at Hummingbird Migration in Fall 2020
Related Articles: Unraveling the Autumnal Journey: A Look at Hummingbird Migration in Fall 2020
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Autumnal Journey: A Look at Hummingbird Migration in Fall 2020. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Autumnal Journey: A Look at Hummingbird Migration in Fall 2020
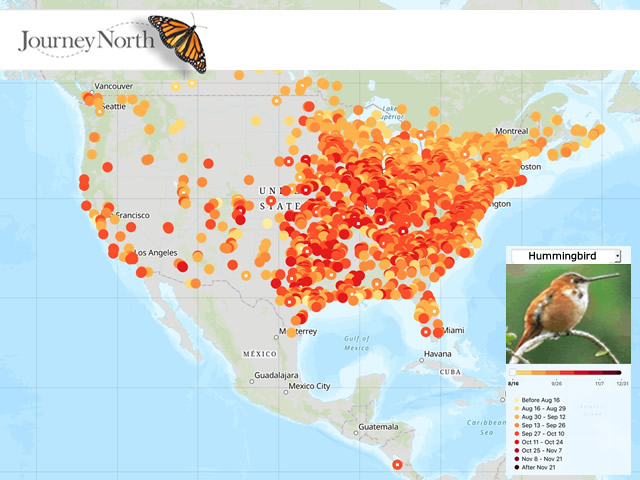
The vibrant colors of autumn signal more than just a change in the season; they herald the beginning of a remarkable natural phenomenon: hummingbird migration. These tiny aerial acrobats embark on an extraordinary journey, traversing thousands of miles to escape the harsh winter conditions of their breeding grounds.
While the precise routes and timing of hummingbird migration can vary from species to species, the fall of 2020 witnessed a captivating display of this annual spectacle. Mapping these migratory patterns provides invaluable insights into the complex lives of hummingbirds, highlighting the intricate interplay of environmental factors, instinctual behaviors, and human impact on their survival.
Navigating the Fall Migration: A Complex Web of Factors
Hummingbirds, known for their remarkable agility and energy, are driven by a combination of instinct and environmental cues to initiate their fall migration. The shortening days, decreasing temperatures, and diminishing food sources trigger a biological shift, prompting them to seek warmer climates and abundant nectar sources.
The Importance of Understanding Migration Patterns
Mapping hummingbird migration in fall 2020, or any year, is crucial for several reasons:
- Conservation Efforts: Understanding migration routes helps identify critical stopover points where hummingbirds rely on specific resources. This information is essential for conservation efforts, ensuring the protection of these vital habitats and promoting sustainable practices.
- Research and Monitoring: Tracking migration patterns provides valuable data for researchers studying hummingbird behavior, population dynamics, and the impact of environmental changes on their survival.
- Citizen Science Engagement: Citizen science programs, where individuals contribute data by reporting hummingbird sightings, play a crucial role in mapping migration routes and informing conservation strategies.
- Education and Awareness: Mapping migration patterns helps raise awareness about the remarkable journeys of hummingbirds, fostering appreciation for these creatures and their role in the ecosystem.
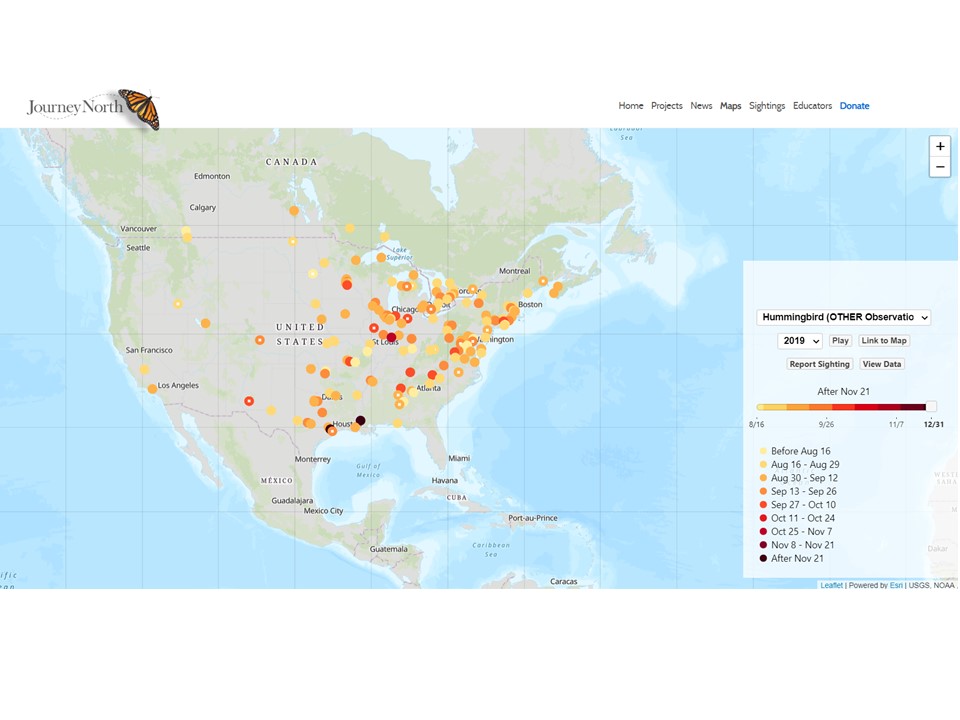
Fall 2020: A Glimpse into Hummingbird Migration
Fall 2020 witnessed a diverse range of hummingbird species embarking on their southward journeys. While data on specific migration routes is constantly evolving, certain patterns emerged:
- Ruby-throated Hummingbirds: This common species, found across the eastern United States, typically migrates to Central America and the Caribbean, utilizing stopover points along the Gulf Coast and Florida.
- Anna’s Hummingbirds: These hummingbirds, primarily found along the Pacific Coast, often remain in their breeding grounds, venturing only short distances to find more favorable conditions.
- Calliope Hummingbirds: This tiny species, the smallest hummingbird in North America, migrates from Alaska and Canada to Mexico and Central America, utilizing diverse stopover points along its route.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into Hummingbird Migration
Q: What are the primary factors that influence hummingbird migration routes?
A: Hummingbird migration routes are influenced by a combination of factors, including:
- Food Availability: The availability of nectar-producing flowers is a primary driver, with hummingbirds seeking out regions with abundant resources.
- Climate and Temperature: Hummingbirds are highly sensitive to temperature changes, migrating to warmer climates to escape the harsh winter conditions.
- Geographic Features: Mountain ranges, coastlines, and other geographical features influence migration routes, as hummingbirds navigate these obstacles and utilize specific corridors.
- Instinctual Behavior: Hummingbirds are guided by an innate sense of direction, passed down through generations, helping them navigate vast distances.
Q: How do hummingbirds find their way during migration?
A: Hummingbirds utilize a combination of navigational tools:
- Visual Cues: They rely on landmarks, such as mountains, rivers, and coastlines, to guide their journey.
- Sun Compass: Like many migratory birds, hummingbirds use the position of the sun to orient themselves.
- Magnetoreception: Some researchers believe hummingbirds possess a magnetic sense, allowing them to detect the Earth’s magnetic field for navigational purposes.
Q: Why is it important to track hummingbird migration patterns?
A: Tracking migration patterns is vital for conservation and research efforts:
- Habitat Conservation: Identifying key stopover points allows for targeted conservation efforts, protecting vital habitats and resources for hummingbirds.
- Population Monitoring: Tracking migration patterns helps scientists assess population trends, identifying potential threats and informing conservation strategies.
- Climate Change Impact: Observing changes in migration patterns can provide insights into the effects of climate change on hummingbird populations and their ability to adapt.
Tips for Supporting Hummingbird Migration
- Provide Nectar Feeders: Offer nectar feeders with sugar-water solutions during the migration season, providing a vital energy source for hummingbirds.
- Plant Native Flowers: Choose native flowering plants that attract hummingbirds, offering a natural and abundant source of nectar.
- Avoid Pesticide Use: Pesticides can harm hummingbirds, so minimize their use in your garden and surrounding areas.
- Protect Natural Habitats: Support organizations dedicated to protecting natural habitats, ensuring that hummingbirds have safe and abundant stopover points.
- Report Sightings: Participate in citizen science programs by reporting hummingbird sightings, contributing valuable data for research and conservation efforts.
Conclusion: Celebrating the Journey
Hummingbird migration in fall 2020, like every year, exemplifies the resilience and beauty of nature. These tiny creatures, driven by instinct and environmental cues, embark on extraordinary journeys, connecting diverse ecosystems and reminding us of the interconnectedness of our planet. By understanding and supporting hummingbird migration, we contribute to the preservation of these remarkable creatures and the vibrant ecosystems they inhabit.

.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Autumnal Journey: A Look at Hummingbird Migration in Fall 2020. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!