Unraveling the Tapestry of Italian: A Comprehensive Look at the Italian Language Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Italian: A Comprehensive Look at the Italian Language Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Italian: A Comprehensive Look at the Italian Language Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Italian: A Comprehensive Look at the Italian Language Map

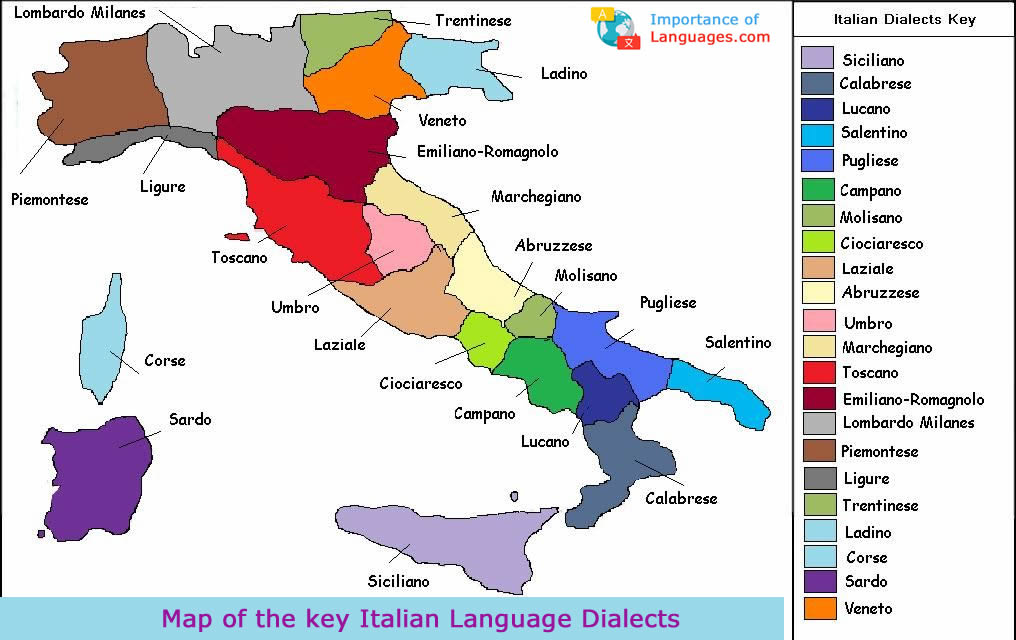
The Italian language, with its melodic cadence and rich history, is a vibrant tapestry woven across the Italian peninsula and beyond. Understanding the nuances of this language requires delving into its geographical distribution, its dialects, and the historical forces that shaped its evolution. This exploration, often visualized through an Italian language map, offers a fascinating glimpse into the linguistic landscape of Italy.
A Visual Journey Through Dialects
The Italian language map is not simply a static representation of geographical boundaries. It serves as a dynamic tool to understand the diverse dialects that flourish across the country. These dialects, often referred to as "regional varieties," are not mere deviations from standard Italian but rather distinct linguistic entities with their own unique grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation.
The Influence of History
The Italian language map reveals a complex interplay of historical events that shaped the linguistic landscape. The Roman Empire, with its widespread use of Latin, laid the foundation for the Romance languages, including Italian. However, after the fall of the empire, regional variations emerged, influenced by local languages, geographic isolation, and political fragmentation.
The Birth of Standard Italian
While dialects thrived, the need for a unified language for communication and cultural expression arose. This led to the emergence of standard Italian, based primarily on the Tuscan dialect, particularly the Florentine variety. This standardization process, initiated during the Renaissance, aimed to bridge the linguistic gap between different regions and facilitate national unity.
Mapping the Dialectal Landscape
The Italian language map provides a visual representation of the distribution of these dialects. It highlights the regions where specific dialectal features are prevalent, revealing the intricate linguistic tapestry of the country. For example, the map might showcase the prevalence of the "open o" pronunciation in the south, contrasting with the "closed o" pronunciation in the north.
Beyond the Peninsula: Italian in the World
The Italian language map extends beyond the borders of Italy, reflecting the global reach of the language. Italian communities scattered across the world, primarily in countries like Argentina, Brazil, and the United States, maintain their linguistic heritage, enriching the global linguistic landscape. These communities often speak dialects that have evolved independently, adding further complexity to the Italian language map.
The Importance of Linguistic Diversity
The Italian language map underscores the importance of linguistic diversity. Recognizing and appreciating the unique characteristics of each dialect fosters cultural understanding and appreciation for the richness of the Italian language. It also highlights the need for language preservation efforts to ensure the continued vitality of these regional varieties.
Navigating the Linguistic Landscape
The Italian language map serves as a valuable tool for language learners and researchers alike. It provides a framework for understanding the nuances of the language, enabling them to navigate the diverse linguistic landscape of Italy and beyond. By understanding the historical context and the geographical distribution of dialects, learners can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and richness of the Italian language.
FAQs about the Italian Language Map
1. What is the difference between Italian and a dialect?
Standard Italian, based on the Tuscan dialect, is the official language of Italy, used in formal settings and media. Dialects, on the other hand, are regional varieties with their own unique features, often spoken in everyday life.
2. How many dialects are there in Italy?
There is no definitive number of Italian dialects, as the boundaries between them are often fluid and overlapping. However, linguists generally recognize a significant number of regional varieties, reflecting the country’s diverse linguistic heritage.
3. Why is the Italian language map important?
The Italian language map provides a visual representation of the linguistic diversity of Italy, highlighting the importance of regional dialects and their historical significance. It also serves as a tool for language learners and researchers to understand the nuances of the language.
4. How has the Italian language map changed over time?
The Italian language map has evolved over time, reflecting changes in dialectal features, the influence of standard Italian, and the impact of migration patterns. The map continues to be a dynamic representation of the linguistic landscape of Italy.
5. What are some examples of dialectal differences?
Dialects can differ in pronunciation, grammar, and vocabulary. For example, the word for "bread" can vary across regions: "pane" (standard Italian), "pa" (Neapolitan), "pan" (Venetian).
Tips for Exploring the Italian Language Map
1. Engage with local communities: Visiting different regions and interacting with local speakers provides firsthand exposure to the nuances of regional dialects.
2. Explore online resources: Websites and interactive maps offer valuable information about the distribution of dialects and their key features.
3. Learn about the history of Italian: Understanding the historical context behind the development of dialects provides a deeper appreciation for their significance.
4. Embrace the diversity: Recognize and appreciate the richness of the Italian language, encompassing both standard Italian and its diverse dialects.
5. Support language preservation efforts: Encourage the use and preservation of regional dialects to ensure the continued vitality of this linguistic heritage.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Language
The Italian language map is a testament to the rich linguistic tapestry of Italy. It reveals the intricate interplay of history, geography, and cultural influences that have shaped the language over centuries. By understanding the nuances of dialects, their distribution, and their historical significance, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of the Italian language. This exploration offers not just a linguistic journey but also a window into the cultural heritage and vibrant identity of Italy.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Italian: A Comprehensive Look at the Italian Language Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!